华西口腔医学杂志 ›› 2018, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 638-645.doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2018.06.011
收稿日期:2018-04-05
修回日期:2018-06-12
出版日期:2018-12-01
发布日期:2018-12-12
通讯作者:
柳忠豪
E-mail:dentlzh@163.com
作者简介:王玉兰,住院医师,硕士,E-mail: ningmengchaxiang@126.com
Yulan Wang,Tiejun Wang,Zhonghao Liu( )
)
Received:2018-04-05
Revised:2018-06-12
Online:2018-12-01
Published:2018-12-12
Contact:
Zhonghao Liu
E-mail:dentlzh@163.com
摘要:
目的 通过锥形束CT(CBCT)测量并分析上颌前突患者上颌切牙内收治疗前后牙根及牙槽骨的变化。方法 选取2014年1月—2015年12月完成的正畸病例37例,其中男性17例,女性20例,平均14.5岁。所有患者拔除上颌双侧第一前磨牙且使用种植钉强支抗内收上颌切牙,通过头影测量获取上颌切牙内收角度、内收量及伸长量,使用NewTom NNT软件对CBCT数据进行多平面重建,调整冠状、轴向与矢状轴,选取通过切缘和根尖的牙齿长轴最长的矢状截面测量上颌切牙内收治疗前后牙根及牙槽骨的变化。结果 上颌前牙内收治疗前后,中切牙内收角度为12.92°±6.43°,内收量为(5.54±2.21) mm,伸长量为(0.60±0.95) mm,牙根吸收长度为(0.81±0.46) mm,牙根吸收率为6.80%±3.60%,切牙内收治疗前后牙根长度变化具有统计学差异(P<0.05),治疗后唇侧牙槽骨高度降低量为(0.20±0.22)mm,治疗前后差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。牙根吸收率与上颌中切牙切端的水平向位移及根尖至唇侧皮质骨的距离具有相关性;唇侧牙槽骨高度变化量与上颌切牙内收角度的相关系数为0.354,具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 上颌前突患者代偿性治疗后,上颌切牙产生了明显的牙根吸收,唇侧牙槽骨高度降低。牙齿移动量越大,或超出了牙槽骨的解剖限制和改建限度,容易导致牙根吸收。唇侧牙槽骨高度变化量与切牙内收角度呈负相关。
中图分类号:
王玉兰,王铁军,柳忠豪. 上颌切牙内收前后牙根及牙槽骨的变化[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2018, 36(6): 638-645.
Yulan Wang,Tiejun Wang,Zhonghao Liu. Changes in root and alveolar bone before and after treatment by retracting the upper incisors[J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2018, 36(6): 638-645.
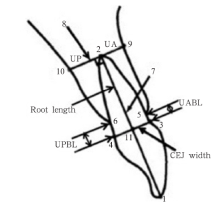
图4
测量参考点/线及测量变量的定义 1:上颌中切牙切缘;2:上颌中切牙根尖;3:唇侧釉牙骨质界;4:舌侧釉牙骨质界;5:唇侧牙槽嵴顶;6:舌侧牙槽嵴顶;7:上颌中切牙牙长轴;8:根尖处牙长轴的垂线;9:根尖处牙长轴垂线与牙槽骨唇侧骨皮质的交点;10:根尖处牙长轴垂线与牙槽骨舌侧骨皮质的交点;11:唇舌侧釉牙骨质界连线与牙长轴的交点;UABL:唇侧牙槽嵴顶到釉牙骨质界的距离,即3和5在平行于7方向上的距离;UPBL:舌侧牙槽嵴顶到釉牙骨质界的距离,即4和6在平行于7方向上的距离;UA:根尖到唇侧骨皮质的距离,即2和9在垂直于7方向上的距离;UP:根尖到舌侧骨皮质的距离,即2和10在垂直于7方向上的距离;Root length:牙根长度,即2和11间的距离;CEJ width:釉牙骨质界宽度,即3和4间的距离。
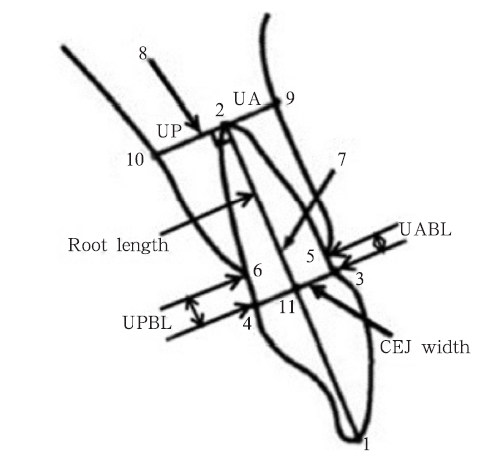
表 1
上颌切牙治疗前后牙根吸收量和各测量值的统计描述
| 测量项目 | T1 | T2 | ΔT(T1-T2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| U1-SN/° | 116.29±5.92 | 103.38±2.92 | 12.92±6.43 |
| U1E-sag/mm | 53.66±3.08 | 48.13±2.40 | 5.54±2.21 |
| U1E-ver/mm | 28.31±1.83 | 28.90±1.38 | -0.60±0.95 |
| UA/mm | 2.49±0.75 | 2.28±0.75 | 0.21±1.03 |
| UABL/mm | 0.88±0.28 | 1.08±0.35 | -0.20±0.22 |
| UPBL/mm | 0.71±0.26 | 0.73±0.31 | -0.02±0.35 |
| Root length/mm | 12.17±0.86 | 11.36±0.91 | 0.81±0.46 |
| 牙根吸收率/% | 6.80±3.60 |
表 3
Pearson相关系数分析
| 分析项目 | 统计量 | ΔTU1-SN | ΔTU1E-sag | ΔTU1E-ver | T2UA | ΔTUA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔTRoot length | r值 | 0.251 | 0.405* | 0.140 | -0.391* | 0.313 |
| P值 | 0.134 | 0.013 | 0.416 | 0.017 | 0.060 | |
| ΔTRoot absorption | r值 | 0.176 | 0.358* | 0.101 | -0.417* | 0.280 |
| P值 | 0.298 | 0.030 | 0.559 | 0.010 | 0.093 | |
| ΔTUABL | r值 | -0.354* | -0.103 | -0.282 | -0.129 | -0.161 |
| P值 | 0.032 | 0.545 | 0.096 | 0.448 | 0.342 |
表 4
典型病例治疗前后头影测量值对比
| 测量项目 | 正常值 | 治疗前测量值 | 治疗后测量值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNA/° | 82.8±4.0 | 87.0 | 87.3 |
| SNB/° | 80.1±3.9 | 81.0 | 80.2 |
| ANB/° | 2.7±2.0 | 6.0 | 7.1 |
| FH-NP/° | 85.4±3.7 | 82.1 | 83.0 |
| NA-PA/° | 6.0±4.4 | 12.6 | 14.9 |
| U1-NA/mm | 5.1±2.4 | 4.8 | -1.2 |
| U1-NA/° | 22.8±5.7 | 22.1 | 8.0 |
| L1-NB/mm | 6.7±2.1 | 6.0 | 6.7 |
| L1-NB/° | 30.3±5.8 | 29.1 | 38.2 |
| U1-L1/° | 125.4±7.9 | 123.9 | 127.4 |
| U1-SN/° | 105.7±6.3 | 109.2 | 95.2 |
| MP-SN/° | 32.5±5.2 | 33.1 | 34.1 |
| MP-FH/° | 31.1±5.6 | 32.0 | 32.2 |
| L1-MP/° | 92.6±7.0 | 96.5 | 104.0 |
| Y轴/° | 66.3±7.1 | 66.4 | 67.1 |
| Pg-NB/mm | 1.0±1.5 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| [1] |
余丽霞, 何姝姝, 陈嵩 . 全景及根尖片对正畸相关牙根吸收诊断准确性的研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2012,30(2):169-172.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1182.2012.02.014 URL |
|
Yu LX, He SS, Chen S . Diagnostic accuracy of orthopan-tomogram and periapical film in evaluating root resorption associated with orthodontic force[J]. West Chin J Stomatol, 2012,30(2):169-172.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1182.2012.02.014 URL |
|
| [2] |
Estrela C, Bueno MR, Leles CR , et al. Accuracy of cone beam computed tomography and panoramic and periapical radiography for detection of apical periodontitis[J]. J Endod, 2008,34(3):273-279.
doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2007.11.023 URL pmid: 18291274 |
| [3] |
Lagravère MO, Carey J, Toogood RW , et al. Three-dimen-sional accuracy of measurements made with software on cone-beam computed tomography images[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2008,134(1):112-116.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2006.08.024 URL |
| [4] |
Veyre-Goulet S, Fortin T, Thierry A . Accuracy of linear measurement provided by cone beam computed tomography to assess bone quantity in the posterior maxilla: a human cadaver study[J]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res, 2008,10(4):226-230.
doi: 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2008.00083.x URL pmid: 18384410 |
| [5] |
Lund H, Gröndahl K, Ken HS , et al. Apical root resorption during orthodontic treatment. A prospective study using cone beam CT[J]. Angle Orthod, 2012,82(3):480-487.
doi: 10.2319/061311-390.1 URL pmid: 2767586 |
| [6] |
Castro IO, Alencar AH, Valladares-Neto J , et al. Apical root resorption due to orthodontic treatment detected by cone beam computed tomography[J]. Angle Orthod, 2013,83(2):196-203.
doi: 10.2319/032112-240.1 URL pmid: 22812378 |
| [7] | Lee AY, Kim YH . Comparison of movement of the upper dentition according to anchorage method: orthodontic mini-implant versus conventional anchorage reinforcement in classⅠmalocclusion[J]. ISRN Dent, 2011: 321206. |
| [8] |
Kim Y, Park JU, Kook YA . Alveolar bone loss around inci-sors in surgical skeletal class Ⅲ patients[J]. Angle Orthod, 2009,79(4):676-682.
doi: 10.2319/070308-341.1 URL pmid: 19537864 |
| [9] |
Nelson PA, Artun J . Alveolar bone loss of maxillary anterior teeth in adult orthodontic patients[J]. Am J Orthod Dento-facial Orthop, 1997,111(3):328-334.
doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(97)70192-6 URL pmid: 9082856 |
| [10] |
Artun J, van’t Hullenaar R, Doppel D , et al. Identification of orthodontic patients at risk of severe apical root resorp-tion[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2009,135(4):448-455.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajodo.2007.06.012 URL pmid: 19361730 |
| [11] |
Simplicio H, da Silva JS, Caldas SG , et al. External apical root resorption in retracted incisors[J]. Orthodontics (Chic), 2012,13(1):86-93.
URL pmid: 22567619 |
| [12] | 马宁, 李巍然, 陈晓红 , 等. 上切牙内收前后的牙根吸收研究[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2015,29(6):330-334. |
| Ma N, Li WR, Chen XH , et al. Root resorption analysis of the maxillary incisors during retraction stage[J]. J Modern Stomatol, 2015,29(6):330-334. | |
| [13] |
许天民 . 青少年期正畸治疗与上中切牙牙根吸收的关系[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2002,37(4):265-268.
doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1002-0098.2002.04.008 URL |
|
Xu TM . The relationship between apical root resorption and orthodontic tooth movement in growing subjects[J]. Chin J Stomatol, 2002,37(4):265-268.
doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1002-0098.2002.04.008 URL |
|
| [14] | de Freitas MR, Soares Beltrão RT, Janson G , et al. Evalua-tion of root resorption after open bite treatment with and without extractions[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2007, 132(2): 143.e15-143.e22. |
| [15] |
Motokawa M, Sasamoto T, Kaku M , et al. Association be-tween root resorption incident to orthodontic treatment and treatment factors[J]. Eur J Orthod, 2012,34(3):350-356.
doi: 10.1093/ejo/cjs064 URL pmid: 23142948 |
| [16] |
Parker RJ, Harris EF . Directions of orthodontic tooth move-ments associated with external apical root resorption of the maxillary central incisor[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 1998,114(6):677-683.
doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(98)70200-8 URL |
| [17] |
Horiuchi A, Hotokezaka H, Kobayashi K . Correlation be-tween cortical plate proximity and apical root resorption[J]. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 1998,114(3):311-318.
doi: 10.1016/S0889-5406(98)70214-8 URL |
| [18] |
Ahn HW, Moon SC, Baek SH . Morphometric evaluation of changes in the alveolar bone and roots of the maxillary anterior teeth before and after en masse retraction using cone-beam computed tomography[J]. Angle Orthod, 2013,83(2):212-221.
doi: 10.2319/041812-325.1 URL pmid: 23066654 |
| [19] |
Vardimon AD, Oren E, Ben-Bassat Y . Cortical bone remo-deling/tooth movement ratio during maxillary incisor retrac-tion with tip versus torque movements[J]. Am J Orthod Den-tofacial Orthop, 1998,114(5):520-529.
doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.05.012 URL pmid: 9810048 |
| [20] |
林薇薇, 陈金武 . 成人前牙内收前后切牙牙槽骨高度变化的研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2014,30(6):823-826.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2014.06.019 URL |
|
Lin WW, Chen JW . Changes in alveolar bone height due to retraction of anterior teeth in adult patients[J]. J Pract Sto-matol, 2014,30(6):823-826.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3733.2014.06.019 URL |
| [1] | 刘晓琳, 任群, 白九平, 康培, 任贵云, 李向军, 冯晓伟. 基于锥形束CT的1 138颗多生牙影像学特征分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(6): 671-677. |
| [2] | 李璐欣, 刘红红, 陈佳, 张志宏, 桑潇, 张莉丽, 王元天. 数字化方法测量种植体周围骨嵴上软组织高度可行性分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(4): 426-433. |
| [3] | 景兵帅, 石冰, 郑谦, 李承浩. 牙槽突裂髂骨松质骨植骨术的效果及影响因素分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(3): 284-289. |
| [4] | 李成蹊, 宋卫健. 上颌侧切牙Ⅱ型和ⅢA型双牙内陷根管治疗1例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(2): 232-236. |
| [5] | 袁婧, 余思静, 游梦, 张琼, 叶玲, 高波. 上颌侧切牙年轻恒牙牙中牙伴根尖周炎的牙髓血运重建治疗1例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2022, 40(6): 716-720. |
| [6] | 鄢梨, 周茂强, 邱嘉旋. 颞下颌关节盘前移位患者关节骨形态与矢状向关节盘位置的关系[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2022, 40(4): 414-421. |
| [7] | 蔡娉娉, 陈熹, 江亦, 卢兆杰, 林捷, 郑志强. 导板与显微镜辅助拆除纤维桩的精确度比较[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2022, 40(3): 297-302. |
| [8] | 江晓娴, 茅传青, 赖永圳, 卢萌, 王承勇, 蔡志宇, 陈伟辉. 替牙期牙槽突裂患者行块状髂骨植骨术的初步疗效分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2022, 40(3): 303-308. |
| [9] | 袁志瑶, 邹习宏, 戴霖霖, 敖慧芝, 李厚轩. 上颌第一磨牙牙根折裂的临床特征分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2021, 39(5): 555-559. |
| [10] | 夏恺, 孙闻天, 余丽媛, 刘钧. 不同快速扩弓装置对牙根吸收影响的系统评价[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2021, 39(1): 38-47. |
| [11] | 郭美玲, 黄臻, 王宠, 王予江. 双侧下颌骨升支矢状劈开截骨后退术对骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者颞下颌关节症状及髁突位置影响的锥形束CT研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(5): 519-524. |
| [12] | 张婷, 陈度, 苗雷英, 谢思静, 汤旭娜. 激光熔融数字化导板技术辅助钙化根管的治疗[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(5): 525-531. |
| [13] | 胡爽, 李春梅, 张帅源, 秦硕, 解晨露, 牛志兴, 孙明磊. 口腔修复膜和β-磷酸三钙治疗颌骨囊肿术后骨缺损的临床价值[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(5): 541-545. |
| [14] | 施雄, 李生娇, 周剑萍, 张利. 低剂量锥形束CT扫描可行性的实验研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(4): 415-418. |
| [15] | 郭彪, 路荣建. 口腔矫治器治疗不同垂直骨面型的骨性Ⅱ类错畸形伴阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征患者上气道形态变化的锥形束CT分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(4): 419-424. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||