| [1] |
康芙嘉, 余磊, 张琦, 李欣鹏, 胡志强, 朱宪春. 隐形矫治器远移下颌第一磨牙的三维有限元研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(4): 405-413. |
| [2] |
任碧晖, 戴婕婷, 徐业豪, 郭水根, 魏洪武, 毛卫华. 下颌骨内表皮样囊肿1例及文献分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(4): 478-482. |
| [3] |
钟嘉伟, 范佩迪, 胡首杉, 高新林, 李奕君, 王军, 熊鑫. 前后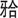 平面与颞下颌骨关节病关系的影像研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(3): 297-304. 平面与颞下颌骨关节病关系的影像研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(3): 297-304. |
| [4] |
吴娟, 苏吉梅, 叶笑味, 徐卫群. 单纯凝血因子Ⅷ补充治愈下颌骨血友病假性肿瘤1例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2022, 40(4): 489-493. |
| [5] |
康泽标, 买晓雪, 王鑫, 谢富强. 计算机辅助游离腓骨下颌骨重建的术后效果评估[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2022, 40(2): 189-196. |
| [6] |
藕小平, 郦芳挺, 吴渺夷. 下颌骨分泌性癌1例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2021, 39(2): 227-229. |
| [7] |
郭美玲, 黄臻, 王宠, 王予江. 双侧下颌骨升支矢状劈开截骨后退术对骨性Ⅲ类错牙合患者颞下颌关节症状及髁突位置影响的锥形束CT研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(5): 519-524. |
| [8] |
范炜, 高德国, 王宇婷, 厉丹丹, 王震东. 阻生下颌第二磨牙下颌骨的三维分析[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(3): 274-279. |
| [9] |
吴建军, 高兴, 王文瑾, Aly Gomaa, 陈洁, 胡雅琴, 翦新春, 蒋灿华. 下颌骨截骨术位置对舌癌患者口腔功能的影响[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(3): 280-283. |
| [10] |
吴家顺, 张伟龙, 李竹风, 王浩帆, 杨肖, 张美, 杨名仲, 陈宇, 汤亚玲. 下颌骨朗格汉斯细胞组织细胞增生症1例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(2): 224-227. |
| [11] |
阚召俊,苏成利,李运峰. 自体喙突移植重建髁突对儿童颞下颌关节强直患者下颌骨生长的远期影响[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2020, 38(1): 23-29. |
| [12] |
马凯,冯元勇,孙阳,尚伟,刘杰,柏娜. 下颌骨腓骨移植联合牙种植术后的覆盖义齿修复1例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2019, 37(3): 336-342. |
| [13] |
叶瑶,李庆祝,涂景秋,雷勇华. 青少年期不同垂直骨面型个别正常下颌骨形态及牙列特征研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2019, 37(1): 76-80. |
| [14] |
金奎镇,徐桥石,王翀,李博,韩正学,冯芝恩. 下颌骨原发腺泡细胞癌1例[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2018, 36(5): 573-575. |
| [15] |
柯星, 李博涵, 陈林林, 姜新娣. 江西成年人群下颌骨体副孔解剖位置的锥形束CT研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2017, 35(6): 607-612. |