West China Journal of Stomatology ›› 2024, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 832-838.doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2024175
Shi Yuan( ), Su Jimei(
), Su Jimei( ), Lü Lihua, Wu Dingwen
), Lü Lihua, Wu Dingwen
Received:2024-05-06
Revised:2024-09-26
Online:2024-12-01
Published:2024-12-04
Contact:
Su Jimei
E-mail:21818483@zju.edu.cn;6198003@zju.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Shi Yuan, Su Jimei, Lü Lihua, Wu Dingwen. A case of hypophosphatemia rickets with unidentified apical periodontitis as the initial symptom of diagnosis[J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2024, 42(6): 832-838.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
Tab 1
Basic information and oral follow-up of the child
| 治疗日期(年龄) | 身高/cm | 磷/(mmol/L) | 碱性磷酸酶/(U/L) | 口腔检查 | 口腔诊断 | 口腔治疗 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2020年9月9日 (3岁) | 89.2 | 0.84 | 1 083 | 51、61、81牙无龋坏,唇侧牙龈瘘管;74牙舌倾,无龋坏,颊侧牙龈瘘管 | 51、61、74、81牙慢性根尖周炎 | 51、61、74、81牙根管治疗,涂氟 |
2020年12月21日 (3岁3月) | 89.2 | 0.77 | 946 | 71牙无龋坏,唇侧牙龈瘘管 | 71牙慢性根尖周炎 | 71牙根管治疗,涂氟 |
2021年5月21日 (3岁8月) | 94.2 | 1.45 | 871 | 51牙充填物存,唇侧牙龈瘘管;55牙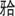 面龋洞 面龋洞 | 51牙慢性根尖周炎,55牙乳牙中龋 | 51牙根管再治疗,55牙充填,涂氟 |
2021年9月9日 (4岁) | 97.9 | 0.76 | 869 | 65牙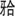 面龋洞 面龋洞 | 65牙乳牙中龋 | 65牙充填,75、85牙窝沟封闭,涂氟 |
2022年3月3日 (4岁6月) | 100.0 | 0.74 | 743 | 无特殊,未见牙龈瘘管 | 无特殊 | 涂氟 |
2023年2月20日 (5岁6月) | 102.0 | 0.86 | 694 | 52牙无龋坏,唇侧瘘管;51牙唇侧陈旧瘘管 | 51、52牙慢性根尖周炎 | 52牙根管治疗,51牙拔除,涂氟 |
2023年5月19日 (5岁9月) | 106.4 | 1.26 | 647 | 71牙残根,71、81牙松动Ⅲ度 | 71、81牙慢性根尖周炎 | 71、81牙拔除,全口涂氟 |
2024年1月12日 (6岁5月) | 106.4 | 1.05 | 708 | 62牙无龋,唇侧牙龈瘘管 | 62牙慢性根尖周炎 | 62牙根管治疗,涂氟 |
| 1 | Huang J, Bao X, Xia W, et al. Functional analysis of a de novo mutation c.1692 del A of the PHEX gene in a Chinese family with X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets[J]. Bone Joint Res, 2019, 8(8): 405-413. |
| 2 | Abdullah A, Wuersching SN, Kollmuss M, et al. X-linked hypophosphatemia: does targeted therapy modify dental impairment[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(24): 7546. |
| 3 | 国家卫生健康委员会, 科学技术部, 工业和信息化部, 等. 关于公布第一批罕见病目录的通知[EB/OL]. [2018-05-11]. . |
| National Health Commission, Ministry of Science and Technology, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, et al. Notice on publishing the first batch of rare disease catalogue[EB/OL]. [2018-05-11]. . | |
| 4 | 中华医学会儿科学分会内分泌遗传代谢学组, 中国罕见病联盟, 中华儿科杂志编辑委员会, 等. 儿童X连锁低磷性佝偻病诊治与管理专家共识[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2022, 60(6): 501-506. |
| The Subspecialty Group of Endocrinologic, Hereditary and Metabolic Diseases, the Society of Pediatrics, Chinese Medical Association, China Alliance of Rare Disea-ses, the Editorial Board of Chinese Journal of Pediatrics, et al. Expert consensus on diagnosis,treatment and management on X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets in children[J]. Chin J Pediatr, 2022, 60(6): 501-506. | |
| 5 | Souza AP, Kobayashi TY, Lourenço Neto N, et al. Dental manifestations of patient with vitamin D-resistant rickets[J]. J Appl Oral Sci, 2013, 21(6): 601-606. |
| 6 | Dahir K, Roberts MS, Krolczyk S, et al. X-linked hypophosphatemia: a new era in management[J]. J Endocr Soc, 2020, 4(12): bvaa151. |
| 7 | Robinson ME, AlQuorain H, Murshed M, et al. Minera-lized tissues in hypophosphatemic rickets[J]. Pediatr Ne-phrol, 2020, 35(10): 1843-1854. |
| 8 | Carpenter TO, Imel EA, Holm IA, et al. A clinician’s guide to X-linked hypophosphatemia[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2011, 26(7): 1381-1388. |
| 9 | Su PH, Yu JS, Wu YZ, et al. Spectrum of PHEX mutations and FGF23 profiles in a Taiwanese cohort with X-linked hypophosphatemia including 102 patients[J]. In Vivo, 2024, 38(1): 341-350. |
| 10 | Zhang C, Zhao Z, Sun Y, et al. Clinical and genetic analysis in a large Chinese cohort of patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia[J]. Bone, 2019, 121: 212-220. |
| 11 | Ma X, Pang Q, Zhang Q, et al. A novel synonymous variant of phex in a patient with X-linked hypophosphatemia[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2022, 111(6): 634-640. |
| 12 | AlJuraibah F, Al Amiri E, Al Dubayee M, et al. Diagnosis and management of X-Linked hypophosphatemia in children and adolescent in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries[J]. Arch Osteoporos, 2021, 16(1): 52. |
| 13 | Zheng B, Wang C, Chen Q, et al. Functional characte-rization of phexgene variants in children with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets shows no evidence of genotype-phenotype correlation[J]. J Bone Miner Res, 2020,35(9): 1718-1725. |
| 14 | Abebe L, Phung K, Robinson ME, et al. Burosumab for the treatment of cutaneous-skeletal hypophosphatemia syndrome[J]. Bone Rep, 2023, 20: 101725. |
| 15 | Senoo S, Fujimoto M, Yamaguchi Y, et al. Switching to burosumab from conventional therapy in siblings with relatively well-controlled X-linked hypophosphatemia[J]. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol, 2024, 33(1): 27-34. |
| 16 | Zhang H, Chavez MB, Kolli TN, et al. Dentoalveolar defects in the hyp mouse model of X-linked hypophosphatemia[J]. J Dent Res, 2020, 99(4): 419-428. |
| 17 | Biosse Duplan M, Coyac BR, Bardet C, et al. Phosphate and vitamin D prevent periodontitis in X-linked hypophosphatemia[J]. J Dent Res, 2017, 96(4): 388-395. |
| 18 | 葛立宏. 儿童口腔医学[M]. 4版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019. |
| Ge LH. Pediatric dentistry[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2019. | |
| 19 | Rabbani A, Rahmani P, Ziaee V, et al. Dental problems in hypophosphatemic rickets, a cross sectional study[J]. Iran J Pediatr, 2012, 22(4): 531-534. |
| 20 | Lira Dos Santos EJ, Nakajima K, Po J, et al. Dental impact of anti-fibroblast growth factor 23 therapy in X-linked hypophosphatemia[J]. Int J Oral Sci, 2023, 15(1): 53. |
| 21 | Jin X, Xu Y, Liu W, et al. Dental manifestations and treatment of hypophosphatemic rickets: a case report and review of literature[J]. BDJ Open, 2023, 9(1): 2. |
| 22 | Steur J, Bohner L, Jackowski J, et al. Oral health and oral-health-related quality of life in people with X-lin-ked hypophosphatemia[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2024, 24(1): 259. |
| 23 | Sabandal MM, Robotta P, Bürklein S, et al. Review of the dental implications of X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets (XLHR)[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2015, 19(4): 759-768. |
| 24 | Marin A, Morales P, Jiménez M, et al. Characterization of oral health status in Chilean patients with X-linked hypophosphatemia[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2021, 109(2): 132-138. |
| 25 | Andersen MG, Beck-Nielsen SS, Haubek D, et al. Periapical and endodontic status of permanent teeth in patients with hypophosphatemic rickets[J]. J Oral Rehabil,2012, 39(2): 144-150. |
| [1] | Li Ying, Feng Xiaoyu, Jia Ruizhi, Wang Yong, Shang Jiajian. Treatment strategies for immature permanent teeth under general anesthesia [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2025, 43(4): 462-468. |
| [2] | Chen Hong, Zhang Ronghua, Zhao Yuan. Non-surgical treatment of maxillary lateral incisor double dens invaginatus type Ⅲ with apical periodontitis [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2024, 42(3): 409-414. |
| [3] | Wang Jun.. Vital pulp therapy of permanent teeth with irreversible pulpitis [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2023, 41(6): 622-627. |
| [4] | Qian Jun, Ma Rui, Qu Yan, Deng Shaochun, Duan Yao, Zuo Feifei, Wang Yajie, Wu Yuwei. Use and performance of artificial intelligence applications in the diagnosis of chronic apical periodontitis based on cone beam computed tomography imaging [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2022, 40(5): 576-581. |
| [5] | Liu Tongxi,Zheng Zhiguo,Yang Jian. Apical barrier technology to treat chronic apical periodontitis caused by type Ⅱ dens invaginatus: a case report [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2019, 37(5): 568-570. |
| [6] | Li Hong, Ji Hai, He Yanyan, Yang Shenghui, Hou Benxiang. Colonization of Porphyromonas endodontalis in primary and secondary endodontic infections [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2015, 33(1): 88-92. |
| [7] | Dong Wei, Li Ren, Wen Liming, Qi Mengchun. Chronic periapical periodontitis of left maxillary first premolar with localized mineralized structure at periapical region: A case report [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2013, 31(2): 211-212. |
| [8] | Shen Jing, Zhang Haifeng, Jin Shufeng, Li Ningning, Fan Jianrong.. One year evaluation of endodontic microsurgery in 54 cases with persistent apical periodontitis [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2012, 30(4): 388-392. |
| [9] | ZHONG Xiao-yi1, YANG Yi-ping2, HEN Wen -xia1, ZHANG Ying -juan1, WEN Chun -mei1. Pulp revascularization of immature anterior teeth with apical periodontitis [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2010, 28(06): 672-674. |
| [10] | LIU Gui-xiang1,2, WANG Qing1, DOU Hui-qin2. Study on the effect of ultrasonic irrigation in deactivating and eliminating the endotoxin in the root canals of chronic periapical periodontitis [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2010, 28(02): 158-161. |
| [11] | LIU Gui -xiang1,2, WANG Qing1, SU Lin-wang1. Endotoxin deactivation in artificial glass root canals with ultrasonic treatment [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2009, 27(03): 280-282. |
| [12] | CAI Yong- hai, LU Chang- shou, HUANG Ke- xiang, CHEN Huan, GAO Jian- yu. Clinical study on acute per iapical per iodontitis caused by over filling [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2008, 26(01): 50-52. |
| [13] | LIU Hong- ying1, LI Wen - yan1, HAO Tai - guo2, GAO Hong- yan1, MA Yue3. Quantitative Study of Effects of Cinnamaldehyde on Levels of Endotoxin in Root Canals in Rats′Per iapical Per iodontitis Model [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2007, 25(03): 233-236. |
| [14] | HUTao,TANHong,XU Yu-dong. Study on Endotoxin Levels of Acute and Chronic Periapical Periodontitis [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2004, 22(01): 52-53. |
| [15] | LIUWeihong*,YUJinhua,ZHOUHongbo,et al.. Changes of Prostaglandin E2Levels in Periapical Exudates after Root Canal Treatment [J]. West China Journal of Stomatology, 2003, 21(01): 39-40. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License.